The Kentucky Office of Medical Cannabis (OMC) released a “How To Guide” outlining requirements for testing and remediation of medical cannabis and medical cannabis products. These standards are designed to ensure the safety and quality of medical cannabis sold to patients. It is critical that all licensees understand the requirements and restrictions in this area.
Batch Sizes and Sampling Requirements
To maintain consistency and traceability, all medical cannabis must be divided into specific batch sizes before testing:
- Harvest Batches: Harvest batches generally may not exceed 20 pounds, except for raw plant material intended for extraction, which can be separated into batches of up to 50 pounds.
- Production Batches: For liquid concentrates, the limit is 5 liters, while the limit for non-liquid material is nine pounds. Finished products for sale cannot exceed 1,000 grams of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Samples from each batch must be collected by an authorized sampler—an employee or agent of a licensed cultivator, processor, producer, dispensary, or safety compliance facility—and submitted to the contracted safety compliance facility for testing.
Testing Standards and Oversight
The Kentucky Cabinet has the authority to inspect, select, collect, and test samples at any time. They may also require businesses to submit samples for testing at their own expense. Safety compliance facilities must maintain accreditation and can only accept samples from authorized individuals.
Before any testing is conducted, a written contract must be established between the medical cannabis business and the safety compliance facility. A copy of such contracts must be provided to the Cabinet within two business days of receipt of the request. Safety compliance facilities are also required to provide their standard operating procedures for sample collection to both the medical cannabis business and the Cabinet.
THC and Contaminant Limits
Kentucky established limits on the amount of delta-9 THC that can be present in medical cannabis and medical cannabis products.
- Raw Plant Material: Maximum delta-9 THC content of 35%
- Concentrates/Edibles: Maximum delta-9 THC content of 70% for concentrates and 10 mg per serving for edibles
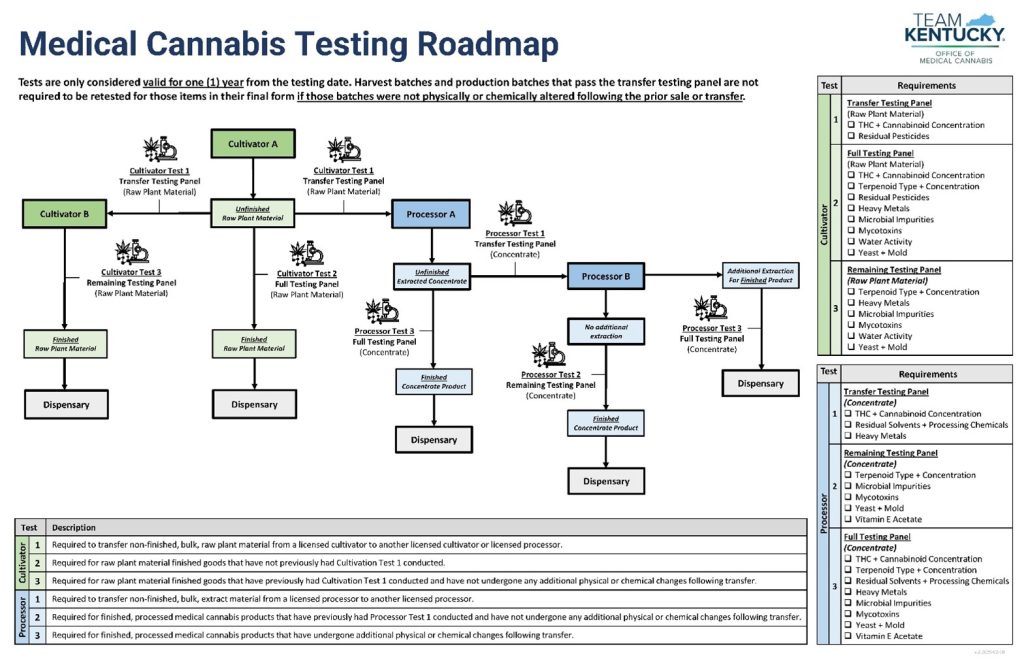
OMC published several resources in addition to the above-referenced “How To Guide” for testing and remediation. For example, the testing roadmap shown below that visually depicts testing requirements and the stages at which cannabis needs to be tested.
Remediation Procedures for Failed Tests
If a batch fails initial testing, remediation is permitted in certain cases, but with strict limitations.
Permitted Remediation:
- Production batches exceeding THC concentration may be remediated to reduce THC levels (harvest batches cannot be remediated for exceeding THC concentration and must be destroyed).
- Batches failing residual solvent or microbial impurity tests may be remediated to reduce solvent levels or sterilize the product.
- Harvest batches failing water activity tests may be further dried or cured.
No toxic or deleterious substance may be imparted into the medical cannabis during remediation, and cultivators and processors must inform safety compliance facilities if a batch has been remediated.
Each batch is allowed only two remediation attempts. If a batch fails after remediation, it must be destroyed in accordance with state regulations.
Importantly, no remediation is allowed for testing failures involving residual pesticides, heavy metals, mycotoxins, yeast and mold, or vitamin E acetate. These batches must be destroyed as medical cannabis waste.
If you have questions about state requirements and/or best practices for testing and remediation or need assistance preparing or reviewing a contract for testing services, please contact a member of our team.


